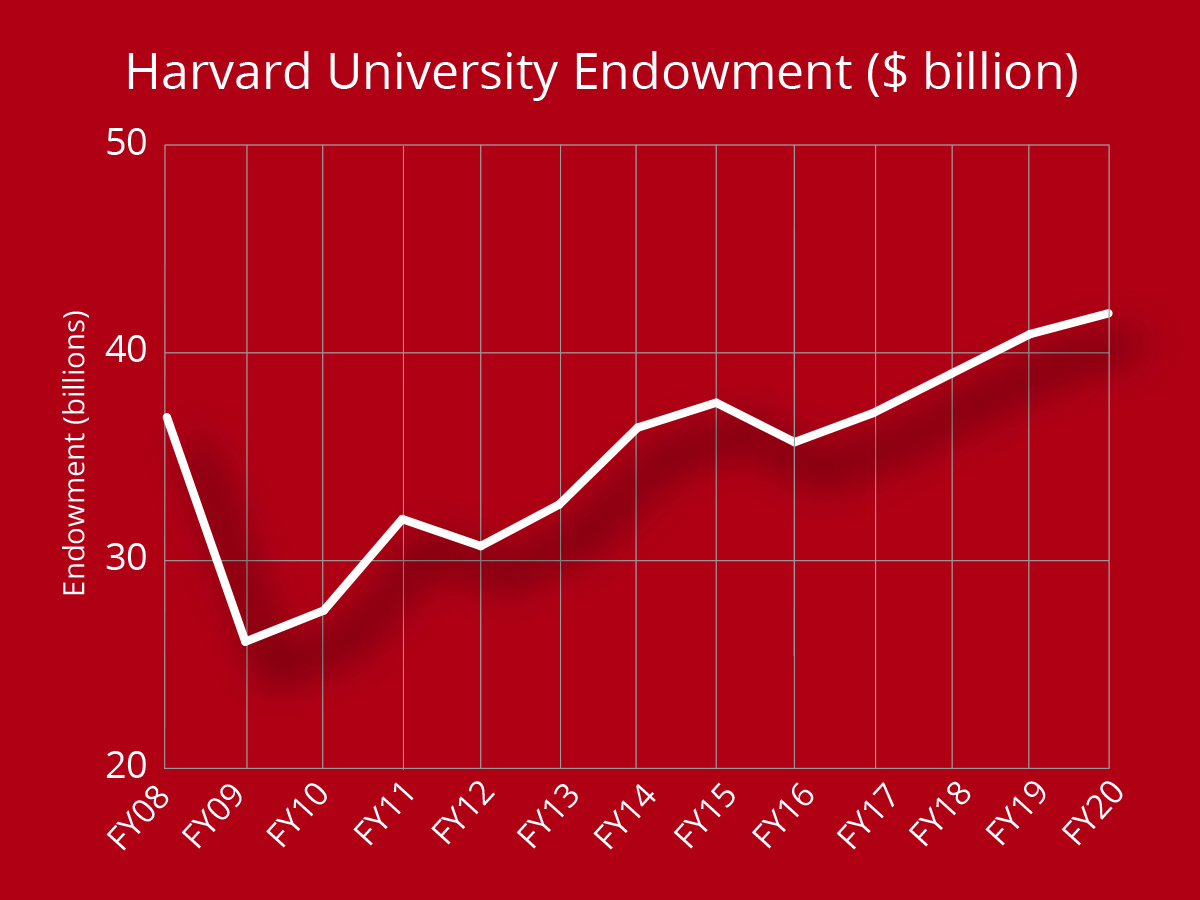
Harvard endowment management plays a crucial role in shaping the financial landscape of Harvard University, boasting a record valuation of $53 billion. This massive financial resource offers both flexibility and challenges, especially when considering donor restrictions and allocation to various University schools. Effectively navigating endowment strategies for universities like Harvard involves a delicate balance between meeting immediate needs and ensuring long-term investments for future sustainability. The impact of endowment on university finances cannot be overstated, as it directly influences everything from operational budgets to the financial aid provided to students. As higher education institutions grapple with financial management in an ever-changing economic climate, understanding the intricacies of Harvard university funding is essential for sustained success.
The management of Harvard’s financial reserves is integral to maintaining the University’s operational integrity and enhancing its academic mission. With total assets exceeding $53 billion, this endowment not only serves as a financial backbone but also faces challenges associated with donor-imposed restrictions and institutional obligations. Navigating investment strategies for educational institutions like Harvard requires a thoughtful approach to both current expenditures and future growth potential. This dynamic underscores the significant effect that these financial reserves have on the University’s overall budget and its commitment to student support programs. As universities worldwide look for innovative methods to optimize their funding sources and ensure financial security, the insights gleaned from Harvard’s approach to managing its endowment can provide valuable lessons.
Understanding Harvard’s Endowment Management
Harvard University’s endowment management plays a critical role in shaping the financial landscape of the institution. With a staggering valuation of $53 billion, the endowment not only supports operational funding but also reflects the complexities of financial management in higher education. A significant portion of this endowment is restricted based on donor specifications, limiting the flexibility that university administrators have in allocating these funds. As such, understanding the balance between long-term investment strategies and immediate financial needs becomes crucial for sustainable practices.
In this context, Harvard’s endowment management strategies must consider various external and internal factors. For example, while leveraging surplus funds during times of financial uncertainty can provide immediate relief, this can lead to pitfalls in long-term budget planning. The necessity for responsible financial management becomes evident as universities, including Harvard, navigate through ongoing fiscal challenges resulting from external shocks such as economic downturns or regulatory changes. By evaluating endowment distributions versus operational costs realistically, Harvard must devise a holistic approach to budget management.
Long-Term Investment Strategies for Universities
The pursuit of long-term investment strategies is essential for universities to ensure their financial stability and growth. Endowment strategies for universities often involve diverse investments that encompass equities, bonds, real estate, and alternative assets. Harvard’s endowment management exemplifies this approach, characterized by a focus on achieving an average return of approximately 8% per year to support its ambitious financial goals. By employing a sophisticated mix of investment assets, institutions can guard against market volatility while capitalizing on growth opportunities over time.
Moreover, the ability to weather financial storms is enhanced through effective long-term investment strategies. Harvard has demonstrated that, while short-term market fluctuations can impact endowment performance, a robust investment strategy mitigates risks associated with economic instability. This underscores the importance of strategic financial management in higher education, as universities leverage their endowments not only to meet current expenses but also to ensure future funding for essential programs, research initiatives, and faculty endowments.
Impact of Endowment on University Finances
The impact of endowment on university finances cannot be overstated. With Harvard’s endowment reaching record levels, it serves as a critical financial backbone that supports various activities within the university environment. However, perceptions often oversimplify the availability of these funds. Many are restricted, which means that, despite the impressive total, only a fraction is readily accessible for general use, ultimately affecting budget allocations and financial planning.
Further complicating the matter, endowment distributions often play a pivotal role in covering operational deficits and funding expansive financial aid programs. As Harvard navigates its fiscal landscape, the revenues generated from the endowment serve multiple purposes, including staff salaries, infrastructure projects, and research grants. The strategy behind allocating endowment earnings reflects the institution’s broader financial management goals, making it essential for leadership to recognize both the benefits and restrictions associated with a substantial endowment fund.
Financial Management Practices in Higher Education
In higher education, effective financial management practices are crucial for ensuring institutional resilience and adaptability. Universities like Harvard are tasked with not only managing large endowments but also navigating the intricacies of budgeting and funding allocation amidst competing priorities. This is particularly relevant during times of financial uncertainty, where carefully crafted financial strategies—such as endowment spending policies—become paramount for maintaining operational stability.
Moreover, financial management in higher education involves a continual reassessment of funding sources and expenditure patterns. Harvard’s leadership must remain proactive in addressing potential budgetary issues while also looking towards future financial sustainability. With the landscape of higher education continually evolving—especially in light of recent policy changes—universities must adopt innovative financial strategies that can withstand economic pressures and position them for long-term success.
Navigating External Financial Challenges
External financial challenges can significantly impact university funding and operations. Harvard’s recent encounters with federal funding reviews exemplify this reality, highlighting the precarious nature of dependently on external financial support. The potential outcomes of losing vital research grants pose a risk that compels university leaders to reconsider their financial strategies and the diversified use of their endowment.
In times of crisis, universities like Harvard may need to adjust their financial management approaches. Options such as temporarily increasing endowment payouts can provide necessary relief, but they also pose risks for the university’s long-term financial health. By adopting a flexible but prudent approach to budgeting, Harvard can better navigate financial challenges while safeguarding its endowment, ensuring future stability and growth.
The Role of Government Funding in Endowment Management
Government funding plays a significant role in the broader context of university endowment management. With many institutions, including Harvard, relying on federal grants and funding to support specific research initiatives, the risk of funding instability can create challenges for financial management. As seen in recent developments, potential changes to government policies can threaten the very foundation upon which universities build their financial plans.
Navigating these complexities requires a strategic alignment between endowment management and government funding. Harvard must creatively integrate these funding sources into its financial framework while being prepared for shifts in the funding landscape. By doing so, the university can better safeguard its operational capacities and ensure continued excellence in education and research.
Endowment Restrictions and Their Implications
Endowment restrictions can impact the overall flexibility of a university’s financial management strategies. At Harvard, a considerable proportion of the endowment is earmarked for specific purposes, such as scholarships, faculty positions, or research initiatives. While these designations are essential for honoring donor intent, they can also limit the institution’s ability to respond to emerging financial needs.
The implications of these restrictions highlight the need for careful planning and prioritization within the university. Leadership at Harvard must navigate these limitations by developing comprehensive budget reports that assess both restricted and unrestricted funds. This strategic approach can help the university allocate resources effectively and ensure that its long-term financial goals remain within reach.
The Future of Harvard’s Endowment and Financial Strategy
Looking ahead, the future of Harvard’s endowment and its financial strategy will largely hinge on the ability of university leaders to adapt their methods in response to changing economic conditions. As the financial landscape becomes increasingly uncertain, there is a pressing need for innovative investment strategies and prudent spending policies that can sustain the university’s mission.
Besides this, the university must focus on forging strong partnerships that enhance its overall financial ecosystem. By cultivating relationships with stakeholders—ranging from alumni to corporate sponsors—Harvard can create new avenues for funding that complement its endowment. As Harvard navigates these challenges, aligning its financial strategy with its educational goals will be paramount for continued success.
The Importance of Effective Communication with Stakeholders
Effective communication with stakeholders is crucial for managing expectations around Harvard’s endowment and financial strategy. Transparency regarding how endowment funds are utilized and the constraints imposed by donor requirements helps build trust among alumni, faculty, and external partners. Encouraging robust conversations around financial strategy foster a deepened understanding of the university’s financial framework and operational necessities.
Moreover, active engagement with the community allows Harvard to cultivate a sense of shared responsibility. Stakeholders become invested not simply in the university’s financial health, but in its broader mission to deliver quality education and research. This acclaimed reputation for fiscal responsibility is essential for attracting donor contributions, which further strengthens the endowment and supports the institution’s goals.
Leveraging Data for Financial Decision-Making
In the age of information, leveraging data analytics for financial decision-making is becoming increasingly integral to university endowment management. Harvard can utilize modeling tools and predictive analytics to forecast investment performance, budget scenarios, and potential risks. This data-driven approach enables the university to adopt more strategic financial management practices that align with long-term objectives.
Additionally, by utilizing data insights, Harvard can enhance its engagement with donors by showcasing the responsible use of funds and the impact on the university’s mission. Demonstrating how financial decisions are informed by analytics ultimately fosters greater accountability and trust within the academic community and its supporters, paving the way for sustained financial health and success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current value of the Harvard endowment and how does it impact university funding?
As of this fiscal year, Harvard’s endowment is valued at a record $53 billion. This vast endowment significantly impacts university funding by providing financial stability and resources for operations, scholarships, research, and construction projects. However, it’s essential to note that a large portion of this endowment is donor-restricted and not fully accessible for immediate use, affecting how Harvard can allocate these funds.
How does Harvard’s endowment management strategy address financial uncertainty?
Harvard’s endowment management strategy includes leveraging funds to mitigate financial uncertainty. This approach helps cover unexpected expenses while recognizing the long-term implications of withdrawing funds for immediate needs. By carefully balancing immediate financial needs with long-term investment strategies, Harvard aims to maintain the endowment’s health and support for the university’s future.
What are the challenges faced in managing the Harvard endowment?
The challenges in managing the Harvard endowment include understanding the restrictions imposed by donors, allocating income for existing operations, and navigating external shocks like economic downturns or policy changes that could impact funding availability. These factors necessitate a prudent approach to financial management in higher education to ensure sustainable growth and support for the university’s mission.
How does the payout rate from the Harvard endowment affect its long-term investment strategy?
The payout rate from the Harvard endowment, approximately 5 percent per year, plays a critical role in its long-term investment strategy. This rate must be carefully balanced to provide sufficient funding for current needs without depleting future resources. Understanding this relationship is vital for Harvard to sustain its financial health and continue to invest in long-term initiatives.
What risks are associated with Harvard’s endowment management during economic downturns?
During economic downturns, Harvard’s endowment management faces multiple risks, including the potential loss of value and revenue, as experienced after the 2009 financial crisis. Additionally, external factors like changes in federal funding and policy changes can further strain resources. Effective endowment management involves planning for these uncertainties to preserve financial stability.
How does Harvard ensure the effective allocation of its endowment funding?
Harvard ensures effective allocation of its endowment funding by adhering to strict guidelines on how restricted funds can be used. These allocations support key operational areas such as scholarships, faculty positions, and research initiatives. The university employs strategic frameworks to analyze budget scenarios, ensuring that expenditures align with both immediate needs and long-term objectives.
What impact does endowment funding have on financial aid at Harvard?
Endowment funding at Harvard has a significant impact on financial aid, enabling the university to offer generous assistance to students. Approximately one-fifth of the annual distribution from the endowment supports financial aid programs, directly benefiting students and making education more accessible. This contribution helps maintain Harvard’s commitment to affordability and support for diverse student populations.
Why is it important for Harvard to balance immediate needs with long-term planning in its endowment management?
Balancing immediate needs with long-term planning in Harvard’s endowment management is crucial for sustaining financial health. Immediate withdrawals can solve short-term budget issues but may deplete future resources needed for ongoing operations and initiatives. A thoughtful approach ensures that the endowment continues to provide stability and support for decades, aligning with the university’s long-term vision.
What role do donors play in Harvard’s endowment management?
Donors play a vital role in Harvard’s endowment management as their contributions often come with specific restrictions on how funds can be used. This impacts financial management in higher education by limiting the university’s flexibility in resource allocation. Understanding donor intent is essential for Harvard to ensure that funds are utilized effectively and align with the university’s overall goals.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Endowment Value | Harvard’s endowment is valued at a record $53 billion, but much is restricted by donors. |
| Restricted Funds | A significant portion of the endowment is tied to specific funds designated for various schools and purposes. |
| Tax Status Risk | Harvard’s tax-exempt status is under scrutiny due to conflicts with governmental policies. |
| Financial Flexibility | Endowments can help address immediate financial needs but also pose long-term risk to resources. |
| Long-term Planning | Strategic planning is essential for balancing current spending and future financial stability. |
| Historical Volatility | Past performance shows significant volatility in returns, necessitating cautious spending. |
Summary
Harvard endowment management involves a complex balancing act between leveraging financial assets for immediate needs and planning for long-term sustainability. The substantial value of Harvard’s endowment may appear reassuring; however, the reality is that much of it is earmarked for specific purposes, limiting available funding for emergent challenges. This necessitates prudent financial strategies to navigate current uncertainties while ensuring that future resources remain intact. Harvard will need to proactively manage both its spending and the external pressures it faces to optimize the utility of its endowment.



